When it comes to inpatient treatment of a range of mental health and mood disorders — from anxiety and depression to schizophrenia, suicidality and acute psychotic episodes — a new study suggest that physical exercise is so effective at alleviating patient symptoms that it could reduce patients’ time admitted to acute facilities and reliance on psychotropic medications. “The general attitude of medicine is that you treat the primary problem first, and exercise was never considered to be a life or death treatment option. Now that we know it’s so effective,…
Read MoreCategory: Health
Skin patch shows promise for children with milk-induced eosinophilic esophagitis
A new study from Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) finds that a skin patch may be useful in treating children with a painful, chronic condition called eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) triggered by milk. Among 20 children with EoE who wore Viaskin Milk — a skin patch measuring just over an inch long containing trace amounts of milk protein — nine (47%) saw an improvement in their symptoms and normalization of their biopsies after 11 months. This is the first study to examine how this treatment, called epicutaneous immunotherapy, may help children…
Read MoreFor people with strong life purpose, making healthier choices may take less effort
Ever wonder how some people seem to meet their fitness goals with ease and love eating healthy foods while others constantly struggle to do either? According to a new study from the Communication Neuroscience Lab at the Annenberg School, people with stronger life purpose are more likely to accept messages promoting health behavior change than those with a weaker sense of purpose. And this might be because they experience less decisional conflict while considering health advice. “Purpose in life has been robustly associated with health in previous studies,” says postdoctoral…
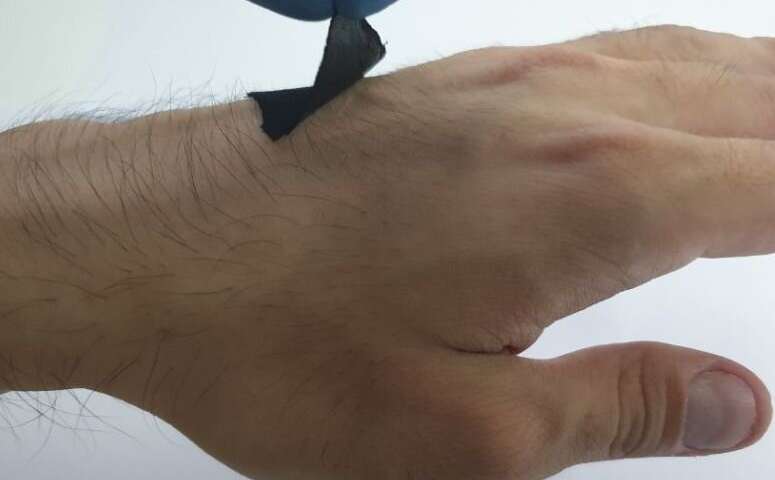
Read MoreOctopus-inspired wearable sensor
Wearable electronics that adhere to skin are an emerging trend in health sensor technology for their ability to monitor a variety of human activities, from heart rate to step count. But finding the best way to stick a device to the body has been a challenge. Now, a team of researchers reports the development of a graphene-based adhesive biosensor inspired by octopus “suckers.” They report their findings in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces. For a wearable sensor to be truly effective, it must be flexible and adhere fully to both wet…
Read MoreHow a member of a family of light-sensitive proteins adjusts skin color
A team of Brown University researchers found that opsin 3 — a protein closely related to rhodopsin, the protein that enables low-light vision — has a role in adjusting the amount of pigment produced in human skin, a determinant of skin color. When humans spend time in the sun without proper skin protection, the sun’s ultraviolet (UV) radiation signals the skin to produce more melanin — which protects against the cancer-causing effects of the radiation — and become darker. There are two parts to solar UV radiation: short wavelength radiation…
Read More