Lisbon, Portugal – 12 April 2019: Prolong your life by increasing your muscle power. That’s the main message of a study presented today at EuroPrevent 2019, a congress of the European Society of Cardiology.1 “Rising from a chair in old age and kicking a ball depend more on muscle power than muscle strength, yet most weight bearing exercise focuses on the latter,” said study author Professor Claudio Gil Araújo, director of research and education, Exercise Medicine Clinic – CLINIMEX, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. “Our study shows for the first time…
Read MoreCategory: Health
Combining genetic and sun exposure data improves skin cancer risk estimates
By combining data on individuals’ lifetime sun exposure and their genetics, researchers can generate improved predictions of their risk of skin cancer, according to findings presented at the American Society of Human Genetics (ASHG) 2018 Annual Meeting in San Diego, Calif. Pierre Fontanillas, PhD, and colleagues at 23andMe, Inc., collected genetic and survey data from over 210,000 consented research participants of European descent. They analyzed the data to identify correlations between previously known and potentially novel skin cancer risk factors and the occurrence of three forms of skin cancer: melanoma,…
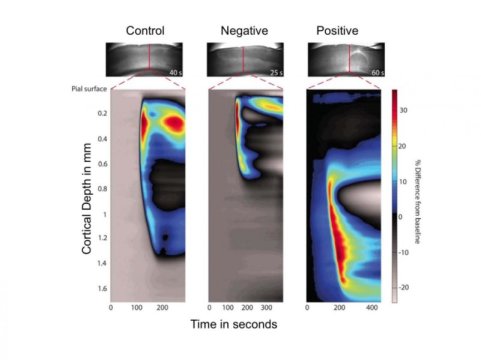
Read MoreYour brain with a migraine: Effect of electric currents
When migraine sufferers see the tell-tale squiggly lines, light flashes and blind spots of a migraine aura, they prepare for a migraine. When researchers see the brain image of an aura, they try to figure out what causes it and if there is a way to stop the start of the migraine. Now an international team of researchers has identified the electrical activity specific to the start of migraines and demonstrated a way to stop it in animal experiments. “Seizures and migraines are two very different states of the brain,”…
Read MoreMove more to live longer
Improving fitness doesn’t require doing activities you don’t like. That’s the main message of research presented today at EuroPrevent 2019. The largest study to date of cardiorespiratory fitness in healthy people found that moving more is linked to living longer, regardless of age, sex, and starting fitness level. “People think they have to start going to the gym and exercising hard to get fitter,” said study author Dr Elin Ekblom-Bak, of the Swedish School of Sport and Health Sciences in Stockholm. “But it doesn’t have to be that complicated. For…
Read MoreBabies born at home have more diverse, beneficial bacteria, study finds
Infants born at home have more diverse bacteria in their guts and feces, which may affect their developing immunity and metabolism, according to a study in Scientific Reports. Understanding why babies born at home have more diverse microbiota for at least a month after birth, compared with those born in a hospital, could help prevent disease later in life. The human microbiome consists of trillions of bacteria, fungi and viruses that live on and in our bodies, many of which benefit our health and prevent chronic conditions such as obesity, diabetes,…
Read More