A nationwide cohort study of all children born in Denmark to Danish-born mothers between 1999 through 2010 concluded that the mumps, measles, and rubella (MMR) vaccine does not increase the risk of autism, does not trigger autism in susceptible children, and is not associated with clustering of autism cases following vaccination. The findings are published in Annals of Internal Medicine. The hypothesized link between measles, mumps, rubella (MMR) vaccine and autism continues to cause concern and challenge vaccine uptake. Currently, there is a concerning increase in measles cases in Europe and…
Read MoreCategory: Health
Go for a run or eat chocolate: A choice dictated by the cannabinoid receptors
Physical inactivity is a common factor in lifestyle diseases — and one that is often linked to the excessive consumption of fatty and/or sugary foods. The opposite scenario of excessive physical activity at the expense of caloric intake can also be harmful, as cases of anorexia nervosa illustrate. These data therefore point to the crucial need to research the neurobiological processes that control the respective motivations for exercise and food intake. A study by Inserm and CNRS researchers published on March 7, 2019 in JCI Insight reveals that the cannabinoid type 1…
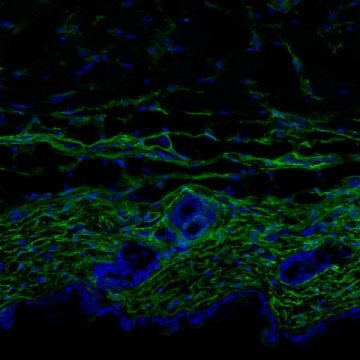
Read MoreSkin ages when the main cells in the dermis lose their identity and function
With age, our tissues lose their function and capacity to regenerate after being damaged. A study published today in Cell by scientists at the Institute for Research in Biomedicine (IRB Barcelona) and the Centro Nacional de Análisis Genómico of the Center for Genomic Regulation (CNAG-CRG) explains how dermal fibroblasts age. The main conclusion drawn is that these fibroblasts lose their cell identity, as if they had “forgotten” what they are, and consequently their activity is altered, thus affecting tissue. The study reveals the cellular and molecular pathways affected by ageing and proposes…
Read MoreCD38 mutation and potential link to autism
Oxytocin has been the focus of intense research around autism spectrum disorder (ASD) due to the hormone’s reported positive effects on anxiety, empathy, social interaction, and maternal behavior. ASD is characterized by early onset of behavioral and cognitive alterations, and by low plasma levels of oxytocin. The enzyme CD38 was recently demonstrated to be critical to the regulation of oxytocin secretion. An animal study published in The FASEB Journal sought to explore whether a deficit in CD38 expression would lead to functional modifications of the brain’s prefrontal cortex, which is involved in…
Read MoreStudy links perimenopause to accelerated fat mass gains, lean mass losses
A UCLA-led study confirms what women approaching menopause have long suspected: menopause does make fat go up. The study finds that women undergoing perimenopause lost lean body mass and more than doubled their fat mass. The research demonstrates that body mass index (BMI) is a very important clinical tool for predicting health events, such as getting diabetes or having cardiovascular disease — but is a less useful gauge of cardio-metabolic risk in older women. The menopause transition, also known as perimenopause, is the time in a woman’s life when hormonal…
Read More