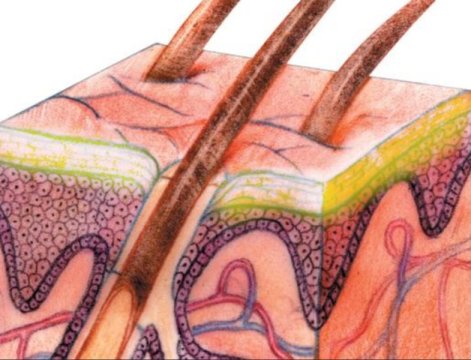
Atopic dermatitis, a common inflammatory skin condition also known as allergic eczema, affects nearly 20 percent of children, 30 percent of whom also have food allergies. Scientists have now found that children with both atopic dermatitis and food allergy have structural and molecular differences in the top layers of healthy-looking skin near the eczema lesions, whereas children with atopic dermatitis alone do not. Defining these differences may help identify children at elevated risk for developing food allergies, according to research published online today in Science Translational Medicine. The research was supported…
Read MoreCategory: Health
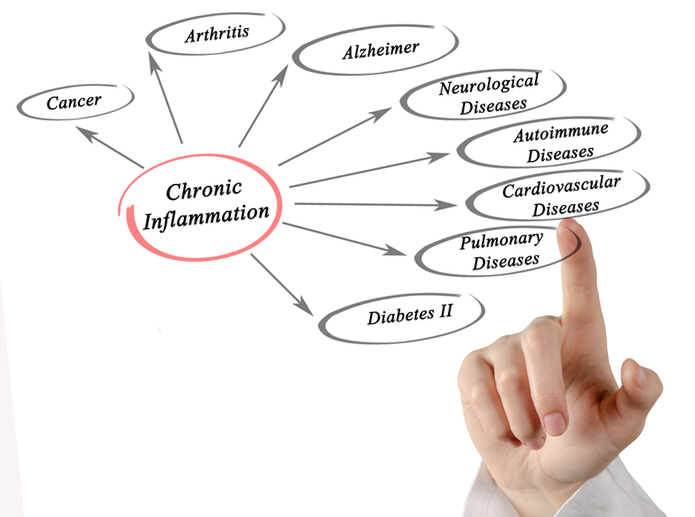
Chronic inflammation in middle age may lead to thinking and memory problems later
People who have chronic inflammation in middle-age may develop problems with thinking and memory in the decades leading up to old age, according to a new study published in the February 13, 2019, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. There are two kinds of inflammation. Acute inflammation happens when the body’s immune response jumps into action to fight off infection or an injury. It is localized, short-term and part of a healthy immune system. Chronic inflammation is not considered healthy. It is a low-grade…
Read MoreMore protein and fewer calories help older people lose weight safely
A high-protein, low-calorie diet helps older adults with obesity lose more weight, maintain more muscle mass, improve bone quality and lose “bad” fat, according to results from a new randomized controlled trial led by Wake Forest University researcher Kristen Beavers. Four research papers based on the study results have been accepted for publication in peer-reviewed journals including the Journals of Gerontology: Medical Sciences and the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. The latest was published this week in the Annals of Nutrition and Metabolism. Geriatricians have long struggled with how to recommend safe weight loss…
Read MoreRealistic exposure study supports the use of zinc oxide nanoparticle sunscreens
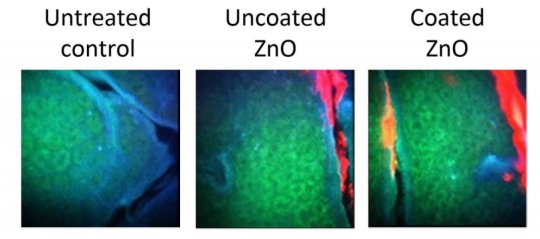
Zinc oxide (ZnO) has long been recognized as an effective sunscreen agent. However, there have been calls for sunscreens containing ZnO nanoparticles to be banned because of potential toxicity and the need for caution in the absence of safety data in humans. An important new study provides the first direct evidence that intact ZnO nanoparticles neither penetrate the human skin barrier nor cause cellular toxicity after repeated application to human volunteers under in-use conditions. This confirms that the known benefits of using ZnO nanoparticles in sunscreens clearly outweigh the perceived…
Read MoreBrain’s primitive sensory region also participates in sophisticated learning
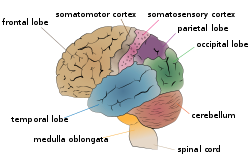
Columbia neuroscientists have revealed that a simple brain region, known for processing basic sensory information, can also guide complex feats of mental activity. The new study involving mice demonstrated that cells in the somatosensory cortex, the brain area responsible for touch, also play a key role in reward learning, the sophisticated type of learning that allows the brain to associate an action with a pleasurable outcome. It is the basis for how we connect our work in the office to that paycheck, or that A+ to the studying we did…
Read More