New therapeutic molecules developed at Toronto’s Centre for Addiction and Mental Health (CAMH) show promise in reversing the memory loss linked to depression and aging. These molecules not only rapidly improve symptoms, but remarkably, also appear to renew the underlying brain impairments causing memory loss in preclinical models. “Currently there are no medications to treat cognitive symptoms such as memory loss that occur in depression, other mental illnesses and aging,” says Dr. Etienne Sibille, Deputy Director of the Campbell Family Mental Health Research Institute at CAMH and lead scientist on…
Read MoreCategory: Health
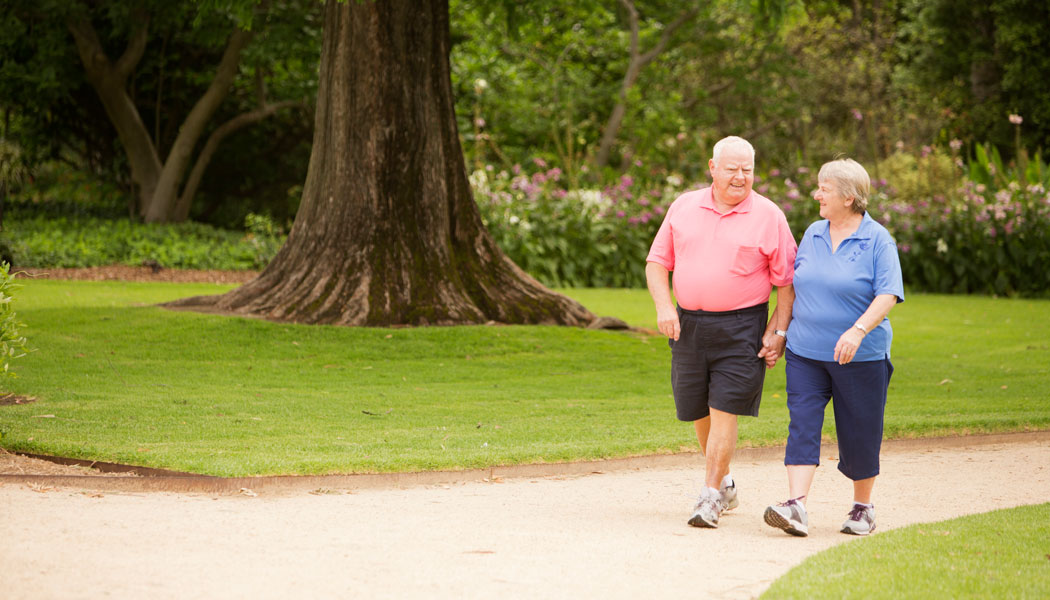
Accelerated risk of mobility loss for people aged 60+ tied to excess weight/inactivity
The combination of excess weight/obesity and an inactive lifestyle represents a powerful joint risk factor for developing mobility loss after age 60, according to a new study. Millions of Americans age 65 and older have difficulty walking, a disability that puts them at high risk of falls and a loss of independence. Other studies had suggested obesity and lifestyle factors such as lack of physical activity played a role in developing this loss of mobility. However, this is the first study to follow participants over time and examine the joint…
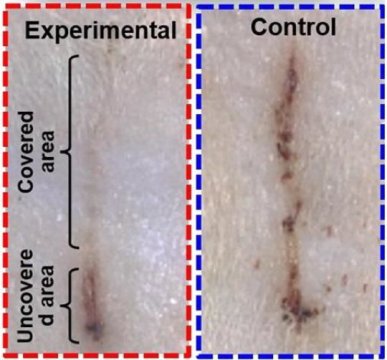
Read MoreE-bandage generates electricity, speeds wound healing in rats
A wound covered by an electric bandage on a rat’s skin (top left) healed faster than a wound under a control bandage (right). Skin has a remarkable ability to heal itself. But in some cases, wounds heal very slowly or not at all, putting a person at risk for chronic pain, infection and scarring. Now, researchers have developed a self-powered bandage that generates an electric field over an injury, dramatically reducing the healing time for skin wounds in rats. They report their results in ACS Nano. Chronic skin wounds include…
Read MoreNew target to prevent, treat alcoholism identified
New research conducted at OHSU in Portland, Oregon, identifies a gene that could provide a new target for developing medication to prevent and treat alcoholism. Scientists at the Oregon National Primate Research Center at OHSU discovered a gene that had lower expression in the brains of nonhuman primates that voluntarily consumed heavy amounts of alcohol compared with those that drank less. Furthermore, the research team unraveled a link between alcohol and how it modulates the levels of activity of this particular gene. Researchers discovered that when they increased the levels…
Read MoreWalking with Pokémon
Augmented reality is when apps and games overlay a real-time camera feed with images, characters and data to provide all kinds of interactive experiences. Pokémon GO is a very popular augmented reality game and University of Tokyo researchers revealed for the first time how the game positively impacted the physical activity in players over 40. They hope the findings will inform urban planners and game designers to inspire people to be more active. In November 2014, Yokohama launched the Yokohama Walking Point Program, which aims to improve people’s health. This…
Read More