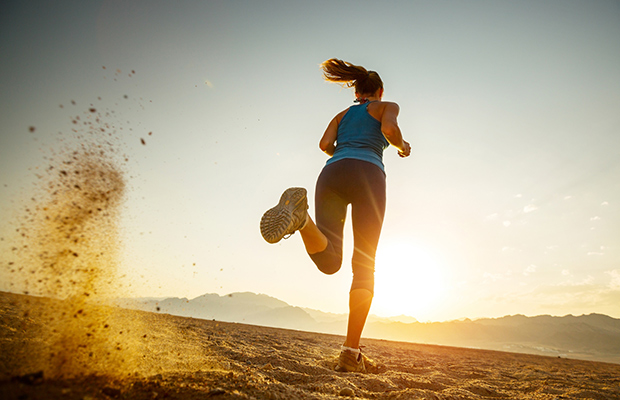
Athletes know a vigorous workout can release a flood of endorphins: “feel-good” hormones that boost mood. Now there’s evidence that exercise produces another hormone that may improve memory and protect against Alzheimer’s disease, according to a study co-led by Ottavio Arancio, MD, PhD, a researcher at Columbia University’s Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons and Taub Institute for Research on Alzheimer’s Disease and the Aging Brain. The study was published in Nature Medicine. Physical activity is known to improve memory, and studies suggest it may also reduce the risk of Alzheimer’s…
Read MoreCategory: Health
Artificial skin could give superhuman perception
A new type of sensor could lead to artificial skin that someday helps burn victims ‘feel’ and safeguards the rest of us, University of Connecticut researchers suggest in a paper in Advanced Materials. Our skin’s ability to perceive pressure, heat, cold, and vibration is a critical safety function that most people take for granted. But burn victims, those with prosthetic limbs, and others who have lost skin sensitivity for one reason or another, can’t take it for granted, and often injure themselves unintentionally. Chemists Islam Mosa from UConn, and James Rusling…
Read MoreBiggest ever map of human Alzheimer’s brain
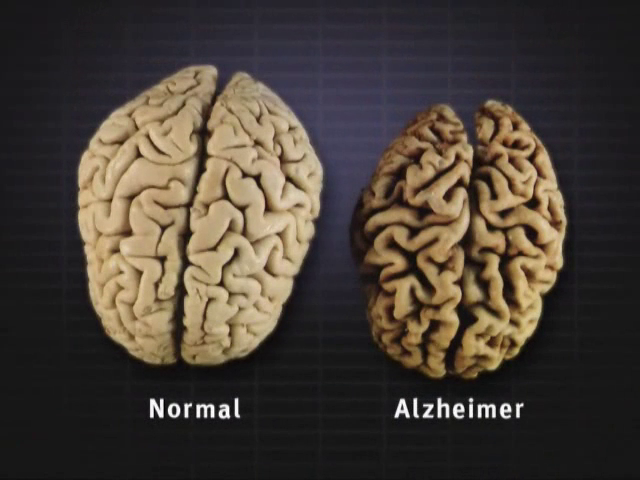
A study of the differences between healthy brains and those with Alzheimer’s Disease has produced largest dataset of its type ever. And the data, developed by a team of researchers led by Dr Richard Unwin at The University of Manchester, is now freely available online for any scientist to use. The team included researchers from the Universities Manchester, Bristol, Liverpool and Auckland. The development is an important advance for scientists researching Alzheimer’s. The team also show that one region of the brain previously thought to be unaffected by the disease,…
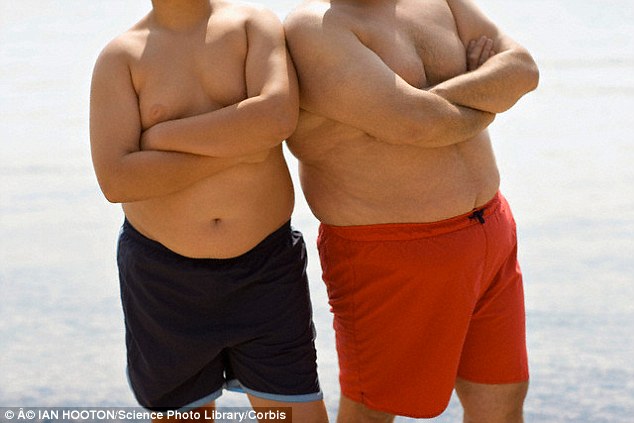
Read MoreExcessive weight gain in early childhood affects teenage heart health
Excessive weight gain in children under two years can lead to cardiovascular and metabolic risk factors in teenage years including increased cholesterol, being overweight and having fat around the middle, finds new research from the University of Sydney. Obesity and cardiovascular risk factors in childhood and adolescence are associated with increased risk of cardiovascular disease in adulthood, the leading cause of death in Australia. Published today in The Journal of Paediatrics, the study tracked the Body Mass Index (BMI) of children from birth to 14 years and found that earlier onset…
Read MoreNew treatment for Chlamydia
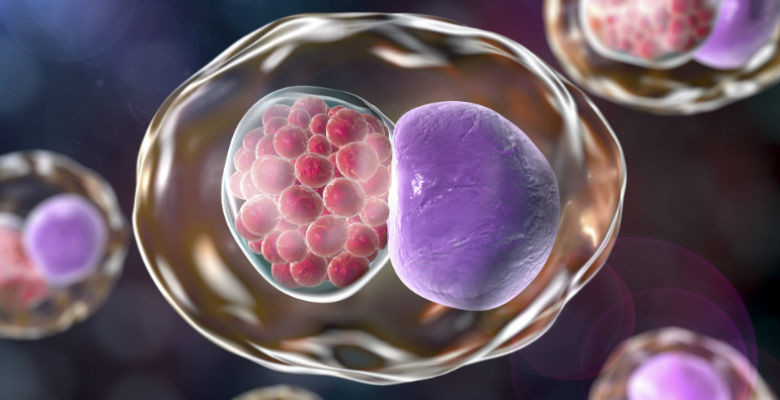
Researchers at the University of Waterloo have developed a new way to prevent and treat Chlamydia, the most common sexually transmitted bacterial infection in the world. The new treatment differs from the traditional anti-biotic treatment as it is a type of gene therapy that is delivered via nanotechnology and is showing a 65 per cent success rate in preventing chlamydia infection on a single dose. “As antibiotic resistance continues to develop, people may experience Chlamydia infections that cannot be treated through conventional means, which is causing increasing public health challenges,”…
Read More