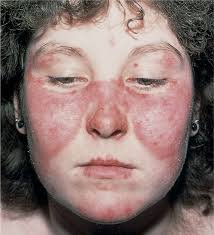
Children with a grave skin disorder known as butterfly syndrome develop severe and chronic blisters. Fibrosis, the thickening and scarring of connective tissues, is a major complication of the disease. Not only can fibrosis lead to club-like appendages where the skin grows over the fingers or toes, but Jefferson’s Andrew South, PhD, an associate Professor in the department of Dermatology and Cutaneous Biology, has shown previously that fibrosis in butterfly syndrome patients also leads to an aggressive form of skin cancer that is often fatal. Now, Dr. South and colleagues…
Read MoreCategory: Health
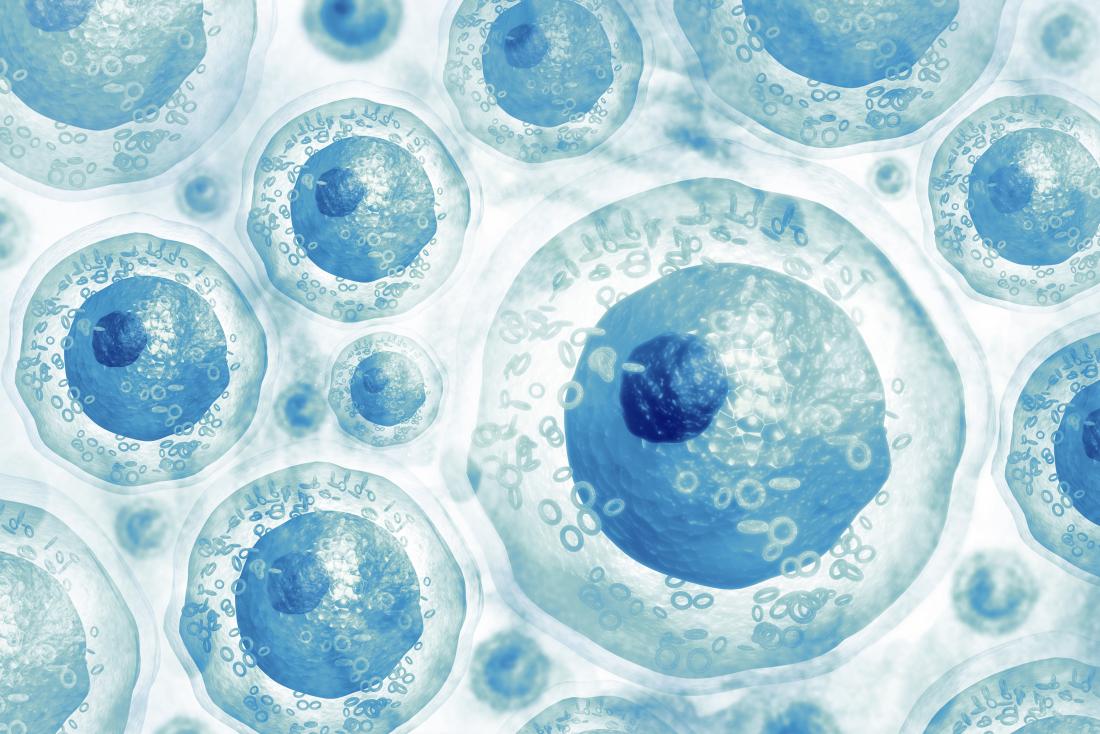
Development of brain stem cells into new nerve cells and why this can lead to cancer
Stem cells are true Jacks-of-all-trades of our bodies, as they can turn into the many different cell types of all organs. This allows the tissues such as muscle or even brain to renew and to heal after injury. This amazing multipotency makes stem cells in the adult body key tools for the future of regenerative medicine. Scientists at the German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ) now publish in the journal Nature how brain stem cells make the decision to transform into new nerve cells. Ana Martin-Villalba and her research team at the German…
Read MoreAmericans concerned about weight, but don’t understand link to heart conditions, health
A Cleveland Clinic survey finds that while most Americans (88 percent) understand that there is a connection between a healthy heart and a healthy weight, most aren’t doing enough — or anything — to combat their own weight issues. The survey found 74 percent are concerned about their weight and 65 percent are worried about getting heart disease due to extra pounds, yet less than half (43 percent) of Americans have tried to make dietary changes to lose weight and 40 percent of those who describe themselves as overweight or…
Read MoreGenetic study provides novel insights into the evolution of skin color
Skin colour is one of the most visible and variable traits among humans and scientists have always been curious about how this variation evolved. Now, a study of diverse Latin American populations led by UCL geneticists has identified new genetic variations associated with skin colour. The study, published in the journal Nature Communications, found that the variation of light skin among Eurasian people evolved independently from different genetic backgrounds. The genetic study analysed pigmentation in over 6,000 Latin Americans, who have a mix of Native American, European and African ancestry. It…
Read MoreWhat you eat could impact your brain and memory
You may be familiar with the saying, “You are what you eat,” but did you know the food you eat could impact your memory? Auriel Willette, assistant professor, and his team of researchers in Iowa State University’s Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition discovered a satiety hormone that, at higher levels, could decrease a person’s likelihood of developing Alzheimer’s disease. A paper outlining the results of their study recently was accepted for publication in Neurobiology of Aging. Using data from the Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI), the researchers looked at…
Read More